Prototype Development: From Concept to Production
Prototype development is essential for turning your ideas into market-ready products. It's not just about creating a model; it's about refining your concept through testing and feedback. Each stage reveals insights that can profoundly affect your final outcome. However, many overlook key techniques or make common mistakes that hinder progress. Understanding these elements can greatly enhance your approach. So, what steps will you take to guarantee your prototype stands out in the competitive landscape?
Key Takeaways
- Prototype development transforms abstract ideas into viable products through iterative design and testing processes.
- Stages include ideation, design, testing, refinement, and pre-production to ensure user needs are met.
- Utilizing techniques like 3D printing and CNC machining enhances precision and efficiency throughout prototyping.
- Engaging users for feedback early on helps identify design flaws and optimize functionality, reducing costly changes.
- Transitioning to manufacturing requires careful evaluation of costs, quality assurance, and continuous market monitoring to ensure product success.
What Is Prototype Development?
Prototype development is an essential phase that bridges the gap between abstract ideas and tangible products, enabling innovators to visualize concepts and make informed decisions.
The prototype development process is integral to the overall product development process, comprising stages like ideation, design, and testing. During the prototyping stage, various types of prototypes—functional, non-functional, high-fidelity, and low-fidelity—are created to assess design and functionality.
This iterative design approach encourages multiple rounds of prototyping and testing, allowing you to refine your product continuously based on user feedback. Effective prototype development confirms both technical feasibility and market appeal, while also preparing detailed design specifications that facilitate a smoother shift to mass production.
Embracing this stage is crucial for turning your vision into reality.
Importance of Prototype Development

While many may overlook the significance of prototype development, it plays a pivotal role in transforming abstract ideas into viable products.
By engaging in prototype testing, you can identify design flaws early, reducing costs and enhancing user experience. A well-crafted product prototype allows you to gather direct feedback, refining your design according to real user needs.
Engaging in prototype testing uncovers design flaws early, cuts costs, and significantly enhances user experience through direct feedback.
Different types of prototypes, such as functional and high-fidelity, are essential for effective design validation at various stages of development. This iterative process not only secures stakeholder buy-in by showcasing feasibility but also guides specifications for manufacturers.
Ultimately, embracing prototype development leads to products that align with market demands, fostering a sense of belonging among users who'll connect with your vision.
Stages of Prototype Development

As you navigate the stages of prototype development, you'll find that each phase—ideation, design, testing, and refinement—plays a vital role in shaping your final product.
Starting with concept generation, you spark creativity and set the groundwork for detailed specifications.
This progression not only enhances your understanding of the product but also guarantees it meets user needs effectively.
Ideation and Concept Generation
In the dynamic landscape of product development, ideation serves as the critical starting point where you generate a wealth of ideas aimed at solving specific market challenges.
Effective ideation hinges on thorough market research, ensuring your product ideas resonate with customer preferences and current trends. Engaging in brainstorming sessions and collaborative workshops can spark creativity, drawing diverse insights from stakeholders.
During this phase, it's essential to identify key functionalities and unique selling propositions that set your product apart from competitors. As you gather ideas, assess their feasibility to align with project goals and resource availability.
This focused approach will streamline your concepts, paving the way for a successful shift to the next stages of prototype development.
Design and Testing Phases
The design and testing phases of prototype development are essential for transforming your initial concepts into viable products.
During the design stage, you'll create detailed plans that guide your prototyping efforts, utilizing techniques like 3D printing and CNC machining to bring your ideas to life.
Once you have a prototype, rigorous testing begins. This process helps you identify structural flaws and usability issues, allowing you to gather critical feedback.
You'll engage in iterative testing, starting with alpha tests using inexpensive materials to verify functionality, followed by beta tests that focus on real user experiences.
Each round of testing informs necessary adjustments, confirming your design is ready for manufacturing and market launch, fostering a sense of community around your innovative creation.
Refinement and Finalization Steps
Once you've gathered feedback from testing, the refinement stage of prototype development becomes essential for enhancing your product.
This is where you focus on refining the product based on user insights, adjusting functionality, aesthetics, and manufacturability.
Iterative testing is key; it allows you to continuously gather feedback and pinpoint weaknesses.
As you refine, make certain you maintain a detailed bill of materials (BOM) to track changes in specifications and components.
The final design should closely resemble what you envision for mass production.
Before moving to full-scale manufacturing, conduct pre-production testing to confirm your design meets regulatory requirements and quality metrics.
This meticulous approach guarantees your prototype isn't just ready but truly optimized for the market.
Techniques for Prototyping
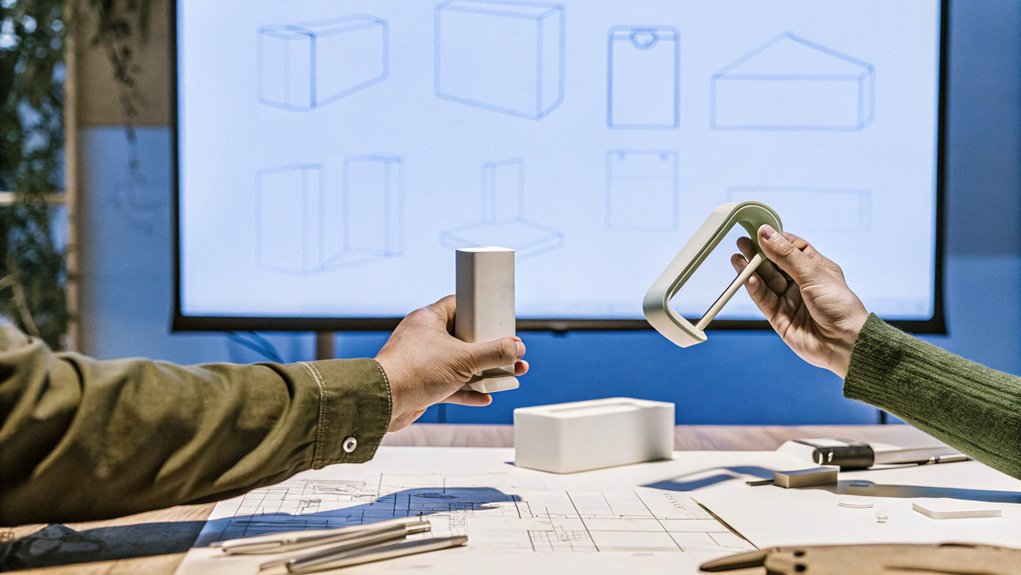

When you explore prototyping techniques, 3D printing stands out for its ability to rapidly produce intricate designs, making it ideal for quick iterations.
On the other hand, CNC machining offers unmatched precision, ensuring that your functional prototypes meet exact specifications.
Understanding the strengths of these methods allows you to effectively choose the right approach for your project's needs.
3D Printing Advantages
While pursuing innovative designs, leveraging 3D printing for rapid prototyping offers a game-changing advantage. This additive manufacturing technique allows you to create complex geometries without traditional tooling, markedly slashing production time and costs.
During the prototyping process, you can quickly produce low-fidelity prototypes, enabling immediate feedback and iteration, which is essential for refining your concepts. The flexibility of materials—ranging from plastics to metals—means you can tailor prototypes for various applications and performance requirements.
Plus, with small batch production capabilities, you can test market responses without large commitments. As advancements continue, these prototypes can achieve high fidelity, closely resembling your final product, which helps stakeholders visualize and assess your design more effectively.
CNC Machining Precision
As you explore advanced prototyping methods, CNC machining stands out for its precision and versatility. This manufacturing process employs computer-controlled tools to achieve remarkable accuracy, with tolerances often within ±0.01 mm.
Whether you're working with metals, plastics, or composites, CNC machining allows you to create functional prototypes that meet your design ambitions. One of its key benefits is the ability to considerably cut down on production time; complex parts can be completed in a fraction of the time compared to manual machining.
Additionally, the capability to perform multiple operations in a single setup enhances efficiency during the prototyping phase. This rapid iteration process is essential for testing concepts and gathering user feedback, ensuring your final product aligns with expectations.
Types of Prototypes
Understanding the various types of prototypes is essential for effectively steering the development process.
You'll encounter functional prototypes, which are working models that demonstrate a product's capabilities, vital for validating design functionality and user interaction.
In contrast, low-fidelity prototypes are simple and inexpensive, allowing for quick concept validation and iterations based on early feedback.
High-fidelity prototypes, on the other hand, closely resemble the final product, making them ideal for user testing and stakeholder presentations.
Additionally, don't overlook pre-production prototypes, the final versions created before mass production, ensuring the design meets all production standards.
Proof of Principle and Iterative Design
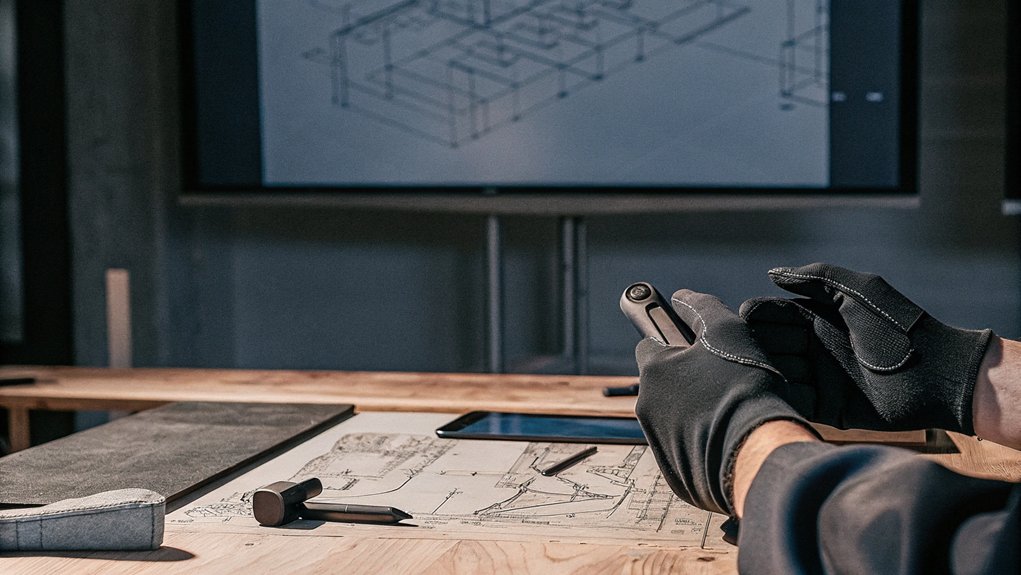

Incorporating proof of principle prototyping into your development process is essential for validating the core functionalities and ergonomics of your product right from the start. This phase serves as your proof of concept, ensuring that the foundation is solid before diving deeper.
Embracing iterative design allows you to refine your prototype continuously, adapting to user feedback and testing results. By gathering insights early, you can identify and rectify design flaws, minimizing costly changes later on.
Each iteration not only enhances the product's functionality and ergonomics but also optimizes manufacturing costs. Engaging users in this process fosters a sense of belonging, ensuring that the final design resonates with their needs and expectations, ultimately leading to a successful launch.
Common Mistakes in Prototyping
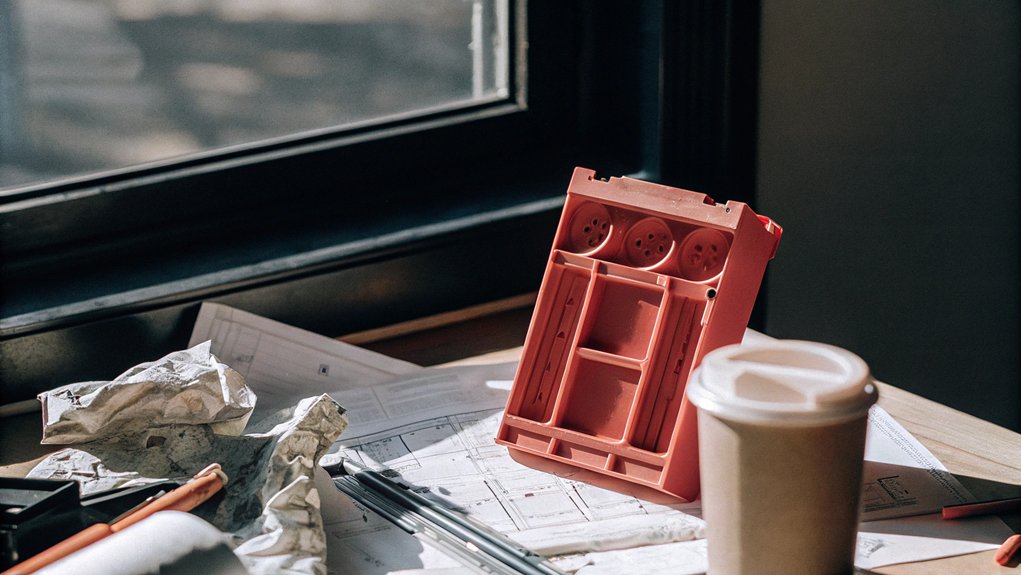

Prototyping is a double-edged sword; while it offers a pathway to innovation, it also presents pitfalls that can derail your project. Many startups rush their prototypes, underestimating the time and effort needed, which leads to a false sense of progress. Failing to seek user feedback early can result in products that miss the mark. Remember, insufficient testing across diverse groups might overlook critical usability issues.
| Common Mistakes | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Rushed Prototypes | Missed design requirements |
| Delayed User Feedback | Products not meeting user needs |
| Lack of Diverse Testing | Overlooked usability issues |
Avoid these pitfalls to create a prototype that truly resonates with users and aligns with your design and manufacturing goals.
Transitioning to Manufacturing

Successfully shifting to manufacturing requires careful evaluation of costs and production efficiency, as even a small oversight can lead to significant delays and increased expenses.
Careful evaluation of costs and production efficiency is essential for a successful shift to manufacturing.
You must prioritize quality assurance to guarantee your product ideas meet regulatory compliance and performance standards before launching.
Consider these essential steps:
- Establish a pre-production approval process to catch defects early.
- Develop a quality plan to communicate acceptable standards to contract manufacturers.
- Engage in thorough testing of components to align with design specifications.
- Monitor the market continuously post-launch to adapt your strategies.
Enhancing Product Appeal and Branding

While developing a product, understanding the Voice of the Customer (VOC) is essential for enhancing its appeal and ensuring it meets market demands. By actively incorporating user feedback, you can refine both aesthetics and functionality, making your final product more desirable. Additionally, effective branding is crucial; integrating sustainability into your design resonates with environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing brand loyalty.
Here's a quick overview of strategies to enhance product appeal and branding:
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| High-fidelity Prototypes | Improves stakeholder buy-in |
| User Feedback | Refines product features |
| Strategic Packaging | Influences consumer perceptions |
Utilizing these approaches not only elevates your product but also solidifies your brand's presence in the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the 5 Stages of Prototyping?
You'll navigate five key stages of prototyping: Alpha, Beta, Pilot, Manufacturing Preparation, and Product Roadmap.
In Alpha, you create initial models to test ideas.
Moving to Beta, you refine designs based on user feedback, ensuring usability.
During the Pilot phase, you finalize material selection and prepare for mass production.
Manufacturing Preparation involves detailed documentation and quality plans, while the Product Roadmap outlines future design iterations, helping you stay aligned with user needs and market trends.
What Is the Transition From Prototype to Production?
Imagine a sculptor chiseling away at marble, refining their masterpiece. The shift from prototype to production mirrors this artistry.
You navigate prototype testing methods, facing production scaling challenges while engaging in design iteration processes. Each step reveals flaws, prompting adjustments that enhance your creation.
What Are the Steps in Prototype Development?
In prototype development, you start with defining the product through research, ensuring it meets user needs.
Next, you move into design iteration, where you refine your initial ideas based on user feedback.
Selecting the right materials is essential during this phase, as it impacts functionality and cost.
Finally, you'll create a high-fidelity prototype, ready for testing and production, ensuring every detail aligns with your vision and market demands.
What Is the Next Stage After Proof of Concept?
What happens after you've proven your idea works? You immerse yourself in the alpha prototype phase.
Here, you'll focus on design iteration, refining both functionality and aesthetics. You'll gather user feedback to guarantee your product resonates with potential users.
This stage is essential for market validation, as it helps you address any flaws before moving forward. By actively testing and adjusting, you set the stage for a successful product that truly meets user needs.
Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of product creation, prototype development weaves together ideas and realities. By maneuvering through stages, employing various techniques, and learning from mistakes, you shape a vision into a viable product. This process isn't just about functionality; it's about crafting an experience that resonates with users. As you shift from prototype to production, remember: every iteration is a step closer to turning dreams into tangible success, ensuring your product shines brightly in a competitive market.